SwiftUI, Apple’s innovative UI toolkit, has transformed the way developers create user interfaces for iOS, macOS, and beyond. One of the fundamental tasks in app development is handling data, and JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a widely-used format for data interchange. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the essentials of loading JSON data in SwiftUI. We’ll start by exploring how to load JSON data directly as a String—useful for quick tests or when dealing with small data payloads. Then, we’ll advance to loading JSON from a file, which is a common scenario for apps that consume complex data structures or large datasets.
Loading JSON as a String
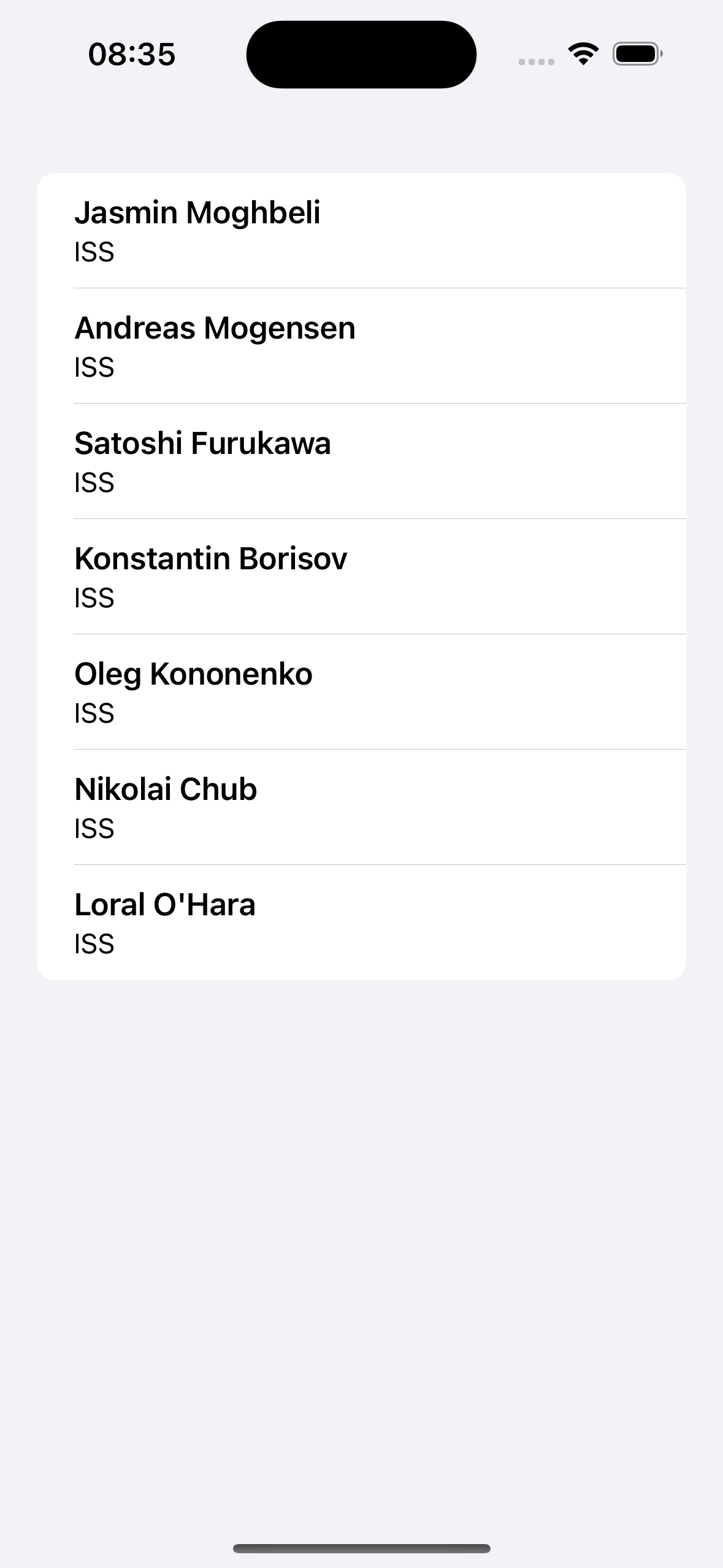
In this example, we’ll import the following JSON data set of current astronauts in space as a string. This data is avaible from this repo of awesome JSON datasets.
{"people": [{"name": "Jasmin Moghbeli", "craft": "ISS"},
{"name": "Andreas Mogensen", "craft": "ISS"},
{"name": "Satoshi Furukawa", "craft": "ISS"},
{"name": "Konstantin Borisov", "craft": "ISS"},
{"name": "Oleg Kononenko", "craft": "ISS"},
{"name": "Nikolai Chub", "craft": "ISS"},
{"name": "Loral O'Hara", "craft": "ISS"}]}
To do this, we first have to create a struct that coheres to the JSON hierarchical structure of the data.
In this case, the hierarchy is an array of people that contains the name and craft of each astronaut.
struct Astronauts: Codable {
let people: [People]
}
struct People: Codable {
let name: String
let craft: String
}
Note the Codable modifier. It is a type alias for the Encodable and Decodable protocols. These protocols allow you to convert yourself into and out of an external representation, such as JSON.
With Codable, you can use the JSONDecoder class to decode JSON data into Swift objects, and then assign those objects to properties in SwiftUI views. This way, you can load JSON data efficiently and update your user interface accordingly.
Now we can import the data as a string:
let input = """
{"people": [{"name": "Jasmin Moghbeli", "craft": "ISS"},
{"name": "Andreas Mogensen", "craft": "ISS"},
{"name": "Satoshi Furukawa", "craft": "ISS"},
{"name": "Konstantin Borisov", "craft": "ISS"},
{"name": "Oleg Kononenko", "craft": "ISS"},
{"name": "Nikolai Chub", "craft": "ISS"},
{"name": "Loral O'Hara", "craft": "ISS"}]}
"""
and decode it:
let data = Data(input.utf8)
let decoder = JSONDecoder()
and finally show the data:
if let astronauts = try? decoder.decode(Astronauts.self, from: data) {
List(astronauts.people, id: \.name) { person in
VStack(alignment: .leading) {
Text(person.name)
.font(.headline)
Text(person.craft)
.font(.subheadline)
}
}
} else {
Text("Failed to load astronauts.")
}
Load JSON from a file
In this section we will load the exact same data, but from a file and not a string variable.
First, copy the data to a file astronauts.json and add it to your Xcode project.
In SwiftUI, you can use Bundle to access files bundled with your app, so we write an extension for it
to decode JSON files:
extension Bundle {
func decode(_ file: String) -> Astronauts {
guard let url = self.url(forResource: file, withExtension: nil) else {
fatalError("Failed to locate \(file).")
}
guard let data = try? Data(contentsOf: url) else {
fatalError("Failed to load \(file).")
}
guard let loaded = try? JSONDecoder().decode(Astronauts.self, from: data) else {
fatalError("Failed to decode \(file).")
}
return loaded
}
}
This makes reading the data extremely easy:
let astronauts = Bundle.main.decode("astronauts.json")
and we can use the same Liststructure as previously to display the data.
